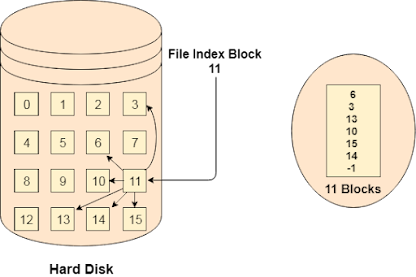
Indexed File Allocation :
Instead of maintaining a file allocation table of all the disk pointers, Indexed allocation scheme stores all the disk pointers in one of the blocks called as indexed block. Indexed block doesn't hold the file data, but it holds the pointers to all the disk blocks allocated to that particular file.
Advantages :
- Supports direct access.
- A bad data block causes the lost of only that block.
Disadvantages :
- A bad index block could cause the lost of entire file.
- Size of a file depends upon the number of pointers, a index block can hold.
- Having an index block for a small file is totally wastage.
- More pointer overhead.
Algorithm :
Step 1: Start.
Step 2: Let n be the size of the buffer
Step 3: check if there are any producer
Step 4: if yes check whether the buffer is full
Step 5: If no the producer item is stored in the buffer
Step 6: If the buffer is full the producer has to wait
Step 7: Check there is any consumer.If yes check whether the buffer is empty
Step 8: If no the consumer consumes them from the buffer
Step 9: If the buffer is empty, the consumer has to wait.
Step 10: Repeat checking for the producer and consumer till required
Step 11: Terminate the process.
Program :
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void main()
{
int f[50], index[50],i, n, st, len, j, c, k, ind,count=0;
clrscr();
for(i=0;i<50;i++)
f[i]=0;
x:printf("Enter the index block: ");
scanf("%d",&ind);
if(f[ind]!=1)
{
printf("Enter no of blocks needed and no of files for the index %d on the disk : \n", ind);
scanf("%d",&n);
}
else
{
printf("%d index is already allocated \n",ind);
goto x;
}
y: count=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d", &index[i]);
if(f[index[i]]==0)
count++;
}
if(count==n)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
f[index[j]]=1;
printf("Allocated\n");
printf("File Indexed\n");
for(k=0;k<n;k++)
printf("%d-------->%d : %d\n",ind,index[k],f[index[k]]);
}
else
{
printf("File in the index is already allocated \n");
printf("Enter another file indexed");
goto y;
}
printf("Do you want to enter more file(Yes - 1/No - 0)");
scanf("%d", &c);
if(c==1)
goto x;
else
exit(0);
getch();
}
Output :
Enter the index block: 5
Enter no of blocks needed and no of files for the index 5 on the disk :
4
1 2 3 4
Allocated
File Indexed
5-------->1 : 1
5-------->2 : 1
5-------->3 : 1
5-------->4 : 1
Do you want to enter more file(Yes - 1/No - 0)1
Enter the index block: 4
4 index is already allocated
Enter the index block: 6
Enter no of blocks needed and no of files for the index 6 on the disk :
2
7 8
A5llocated
File Indexed
6-------->7 : 1
6-------->8 : 1
Do you want to enter more file(Yes - 1/No - 0)0
Comments
Post a Comment